THE
MAASAI PEOPLE
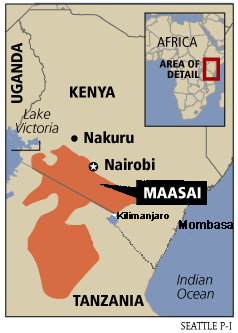 The
Maasai people of East Africa live in southern Kenya and northern
Tanzania along the Great Rift Valley on semi-arid and arid
lands. The Maasai occupy a total land area of 160,000 square
kilometers with a population of approximately one half million
people. However, many Maasai see the national census as government
meddling and often miscount their numbers to census takers.
The
Maasai people of East Africa live in southern Kenya and northern
Tanzania along the Great Rift Valley on semi-arid and arid
lands. The Maasai occupy a total land area of 160,000 square
kilometers with a population of approximately one half million
people. However, many Maasai see the national census as government
meddling and often miscount their numbers to census takers.
The
Maasai society is comprised of sixteen sections (known in
Maasai as Iloshon): Ildamat, Ilpurko, Ilkeekonyokie, Iloitai,
Ilkaputiei, Ilkankere, Isiria, Ilmoitanik, Iloodokilani, Iloitokitoki,
Ilarusa, Ilmatatapato, Ilwuasinkishu, Kore, Parakuyu, and
Ilkisonko, also known as Isikirari (Tanzania's Maasai). There
was also once Iltorobo section but was assimilated by other
sections. A majority of the Maasai population lives in Kenya.
Sections such as Isikirari, Parakuyu, Kore and Ilarusa lives
in Tanganyika.
Homestead
and labor
 The
Maasai live in Kraals arranged in a circular fashion. The
fence around the kraal is made of acacia thorns, which prevent
lions from attacking the cattle. It is a man's responsibility
to fence the kraal. While women construct the houses. Traditionally,
kraals are shared by an extended family. However, due to the
new land management system in the Maasai region, it is not
uncommon to see a kraal occupied by a single family.
The
Maasai live in Kraals arranged in a circular fashion. The
fence around the kraal is made of acacia thorns, which prevent
lions from attacking the cattle. It is a man's responsibility
to fence the kraal. While women construct the houses. Traditionally,
kraals are shared by an extended family. However, due to the
new land management system in the Maasai region, it is not
uncommon to see a kraal occupied by a single family.
The
Inkajijik (maasai word for a house) are loaf-shaped and made
of mud, sticks, grass, cow dung and cow's urine. Women are
responsible for making the houses as well as supplying water,
collecting firewood, milking cattle and cooking for the family.
Warriors are in charge security while boys are responsible
for herding livestock. During the drought season, both warriors
and boys assume the responsibility for herding livestock.
The elders are directors and advisors for day-to-day activities.
Every morning before livestock leave to graze, an elder who
is the head of the inkang sits on his chair and announces
the schedule for everyone to follow.
The
Maasai are a semi-nomadic people who lived under a communal
land management system. The movement of livestock is based
on seasonal rotation. Contrary to many claims made by outsiders,
particularly the Hardinian school of thought, this communal
land management system allows us to utilize resources in a
sustainable manner. Each section manages its own territory.
Under normal conditions, reserve pastures are fallowed and
guarded by the warriors. However, if the dry season becomes
especially harsh, sections boundaries are ignored and people
graze animals throughout the land until the rainy season arrives.
According to Maasai traditional land agreement, no one should
be denied access to natural resources such as water and land.
Subsistence
economy
Livestock
such as cattle, goats and sheep are the primary source of
income for the Maasai. Livestock serves as a social utility
and plays an important role in the Maasai economy. Livestock
are traded for other livestock, cash or livestock products
such as milk and siege. Individual, families, and clans established
close ties through giving or exchange of cattle. "Meishoo
iyiook enkai inkishu o-nkera"- so goes a Maasai
prayer. The English translation of this praye is: "May
Creator give us cattle and children. Cattle and children are
the most important aspect of the Maasai people.
Maasai
economy with outsiders
The
Maasai economy is increasingly dependent on the market economy.
Livestock products are sold to other groups in Kenya for the
purchase of beads, clothing and grains. Cows and goats are
also sold for uniform and school fees for children. It is
now common to see young Maasai men and women in major towns
and cities of Kenya selling, not just goats and cows, but
also beads, cell phones, chacoal, grain among other items.
The entrepreneurial spirit is something new in our society.
It
was not until the early 1980s with the Group Ranch project
that we became much more entrenched in a market economy and,
hence, more impoverished generally speaking.
Maasai
diet
Traditionally,
the Maasai rely on meat, milk and blood from cattle for protein
and caloric needs. People drink blood on special occasions.
It is given to a circumcised person (o/esipolioi), a woman
who has given birth (entomononi) and the sick (oltamueyiai).
Also, on a regular basis drunk elders, ilamerak, use the blood
to alleviate intoxication and hangovers. Blood is very rich
in protein and is good for the immune system. However, its
use in the traditional diet is waning due to the reduction
of livestock numbers.
More
recently, the Maasai have grown dependent on food produced
in other areas such as maize meal (unga wa mahindi), rice,
potatoes, cabbage (known to the Maasai as goat leaves), etc.
The Maasai who live near crop farmers have engaged in cultivation
as their primary mode of subsistence. In these areas, plot
sizes are generally not large enough to accommodate herds
of animals; thus the Maasai are forced to farm. Our people
traditionally frown upon this. Maasai believe that tilizing
the land for crop farming is a crime against nature. Once
you cultivate the land, it is no longer suitable for grazing.
Private
ownership
The
concept of private ownership was, until recently, a foreign
concept to the Maasai. However, in the 1960s and 1980s, a
program of commercializing livestock and land was forced on
us initially by the British and later by the government of
Kenya. Since then, our land has been subdivided into group
and individual ranches. In other parts of Maasailand people
subdivided their individual ranches into small plots, which
are sold to private developers.
The
new land management system of individual ranches has economically
polarized our people; some Maasais, as well as outside wealthy
individuals, have substantially increased their wealth at
the expense of others. The largest loss of land, however,
has been to national parks and reserves, in which the Maasai
people are restricted from accessing critical water sources,
pasture, and salt lick. Subdivision of Maasailand reduced
land size for cattle herding, reduced the number of cows per
household, and reduced food production. As a result, the Maasai
society, which once was a proud and self-sufficient society,
is now facing many social-economic and political challenges.
The level of poverty among the Maasai people is beyond conceivable
height. It is sad to see a society that had a long tradition
of pride being a beggar for relief food because of imposed
foreign concepts of development.
The
future of the Maasai is uncertain at this point. One thing, however, is certain that the Maasai culture is quickly eroding at the expense of civilization.


 The
Maasai people of East Africa live in southern Kenya and northern
Tanzania along the Great Rift Valley on semi-arid and arid
lands. The Maasai occupy a total land area of 160,000 square
kilometers with a population of approximately one half million
people. However, many Maasai see the national census as government
meddling and often miscount their numbers to census takers.
The
Maasai people of East Africa live in southern Kenya and northern
Tanzania along the Great Rift Valley on semi-arid and arid
lands. The Maasai occupy a total land area of 160,000 square
kilometers with a population of approximately one half million
people. However, many Maasai see the national census as government
meddling and often miscount their numbers to census takers.
 The
Maasai live in Kraals arranged in a circular fashion. The
fence around the kraal is made of acacia thorns, which prevent
lions from attacking the cattle. It is a man's responsibility
to fence the kraal. While women construct the houses. Traditionally,
kraals are shared by an extended family. However, due to the
new land management system in the Maasai region, it is not
uncommon to see a kraal occupied by a single family.
The
Maasai live in Kraals arranged in a circular fashion. The
fence around the kraal is made of acacia thorns, which prevent
lions from attacking the cattle. It is a man's responsibility
to fence the kraal. While women construct the houses. Traditionally,
kraals are shared by an extended family. However, due to the
new land management system in the Maasai region, it is not
uncommon to see a kraal occupied by a single family.